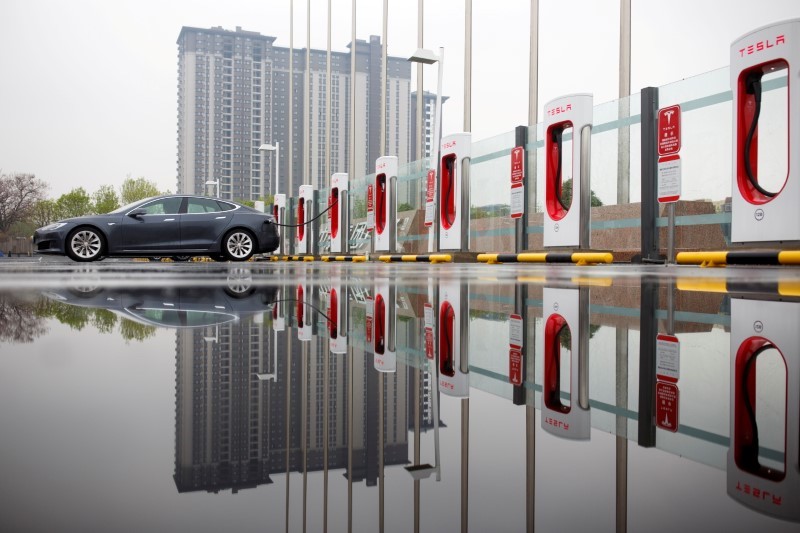
Australia announced this week it will introduce new standards targeting vehicle emissions to boost the uptake of electric cars.
Energy Minister Chris Bowen told a news conference the move aims to bring the country into line with other developed economies.
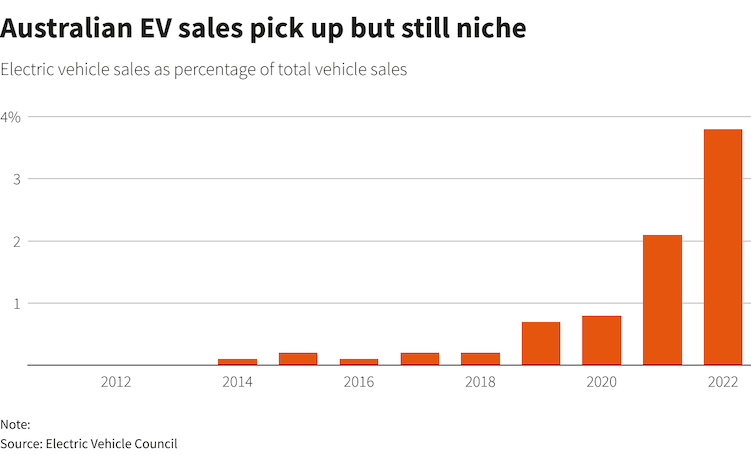
Just 3.8% of cars sold in Australia last year were electric, well behind economies such as Britain and Europe, where electric cars made up 15% and 17% of sales, respectively.
The new national electric vehicle strategy will introduce a fuel efficiency standard that will outline how much carbon dioxide a car will produce when running.
“Fuel-efficient and electric vehicles are cleaner and cheaper to run – today’s announcement is a win-win for motorists,” Bowen said in a statement. Details would be finalised in the coming months, he added.
ALSO SEE:
US Has No Plan to ‘Decouple’ with China, Yellen Says
Move could save motorists $519 a year
Apart from Russia, Australia was the only developed country to either not have or be developing fuel efficiency standards, which encourage manufacturers to supply more electric and no-emission vehicles.
Transport is the third largest source of carbon emissions in Australia – one of the world’s biggest emitters on a per capita basis.
The initiative will help cut the country’s emissions by at least 3 million tonnes of carbon by 2030, and over 10 million tonnes by 2035, Bowen said.
The Electric Vehicle Council (EVC) welcomed the move but said Australia must bring in strong standards or “remain the world’s dumping ground for dated, high-emission vehicles,” chief executive Behyad Jafari said.
On average, new cars in Australia use 40% more fuel than the European Union and 20% more than the United States, with studies showing the introduction of a fuel efficiency standard could save motorists A$519 ($349) per year, Bowen said.
Greens party leader Adam Bandt said the government’s strategy needs to accelerate and needs electric vehicle targets as well as the fuel efficiency standards.
EV demand rising
Demand for electric vehicles is growing in Australia, although supply has not kept up with demand in the absence of incentives for automakers.
Australia’s centre-left Labor government last year flagged plans to introduce new regulations to increase sales of electric cars.
Prime Minister Anthony Albanese, who won power last year on a promise of climate policy reforms, cut taxes for electric vehicles and raised Australia’s 2030 target for cutting carbon emissions to a 43% reduction from 2005 levels.
The initiatives came after about a decade of inaction under the previous Liberal government, which set Australia behind all its peers.
‘Way behind rest of the world’
Former Prime Minister Scott Morrison said in 2019 that policies to reduce vehicle emissions would “end the weekend”, while other critics said it would be a death knell for popular utility vehicles, or utes, used by builders and farmers.
Bowen acknowledged more needs to be done on infrastructure to charge EV cars.
There are about 83,000 EVs on Australian roads and as at December 2022, there were just over 4,900 public chargers located at fewer than 2,400 sites.
“We’re way behind the rest of the world again,” Bowen said in a radio interview later in the day.
“We are fixing that. We’ve got a policy of putting in a fast charger once every 150 kilometres on the highway. I’ll be saying more about that pretty soon,” he said.
- Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO SEE:
China Invites Australian PM to Visit Beijing This Year – SCMP
Australia Bans TikTok Risking Ongoing Trade Talks With China
Australia Expects 60% of Coal Power Output to Cease by 2030























