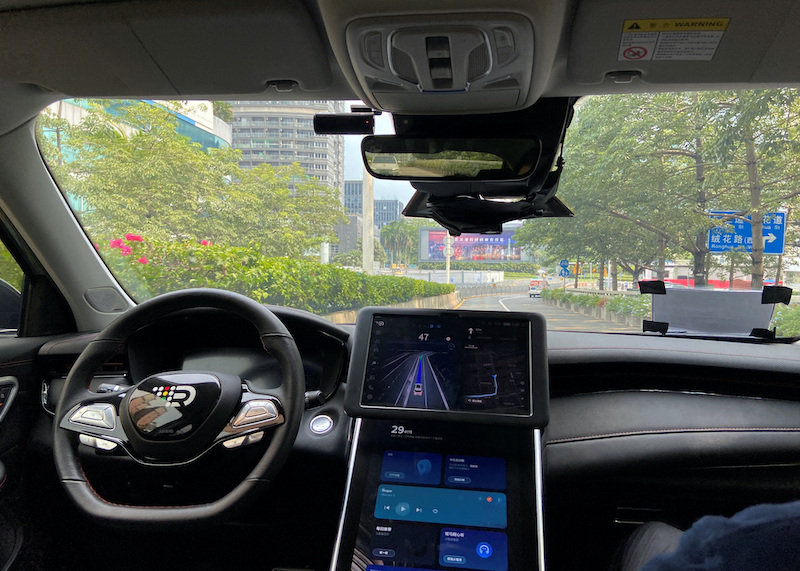
China tech conglomerate Baidu said on Monday it has been awarded permits to operate driverless robotaxi services on open roads in two Chinese cities.
The permits – which do not require human safety drivers in the car – allow commercial robotaxis to offer rides to the public in specific parts of Chongqing and Wuhan.
The company said the licences, which took effect on Monday, marked a “turning point” in China’s policy-making towards autonomous driving.
“These permits have deep significance for the industry,” Wei Dong, chief safety operation officer of Baidu’s Intelligent Driving Group, said in an interview. “If we think of the exploration of space, this moment is equal to landing on the moon.”
At first, Baidu will deploy a batch of five fee-charging robotaxis in each city, where they will be allowed to operate in designated areas from 9am to 5pm in Wuhan and 9:30am to 4:30pm in Chongqing, the company said in a statement.
The service areas span 30 square km (11.6 square miles) in Chongqing’s Yongchuan District and 13 sq km in the Wuhan Economic & Technological Development Zone.
ALSO SEE: Sino-Russian Trade Boom Continues, China Exports up 22%
Robotaxis Start in Low-Traffic Areas
In April, Baidu‘s Apollo and Toyota Motor-backed Pony.ai said that they received permits in Beijing to deploy robotaxis without safety drivers in the driver’s seat on open roads within a 60 sq km area.
But the Beijing permits still require them to have a safety driver in the passenger seat. These services have started.
Baidu is also in talks with local governments in Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen, to secure licences within a year to test fully-driverless and unpaid robotaxis in those cities, according to Wei.
China should adopt autonomous vehicles in passenger transport with care, the country’s Ministry of Transportation said in drafted rules to regulate the self-driving industry.
The ministry will encourage the use of autonomous vehicles as taxis in easily controlled scenarios in low traffic situations, according to a draft seeking public advice published on Monday.
“The management of transportation with autonomous driving vehicles should stick to the principles with safety as the top priority,” the Ministry of Transportation said in the drafted rules.
US Regulators Also Pushing Ahead
China and the US are in a race to commercialise autonomous driving, from cutting-edge technologies in sensors and mapping to regulations balancing between development and safety.
US states like Arizona have been allowing self-driving trucking companies to operate without human drivers, while California gave approval in June for General Motor’s robotaxi unit Cruise to start charging passengers for its driverless rides.
In January, Cruise got a permit from the California Public Utilities Commission that allowed it to offer paid and fully driverless rides from 10pm to 6am in select streets in San Francisco.
Meanwhile, Apollo Go – Baidu‘s robotaxi service – has operated over 1 million rides across 10 Chinese cities since its launch in 2020.
Baidu has not reported any problems with the service and has not given a breakdown for how much it has invested in the project.
- Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO SEE:
Baidu Joins Pony.ai in Planned Beijing Robotaxi Surge
Geely Launches Satellites for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation
Waymo Kicks Off Fully Autonomous Rides – The Information
VW Seen In Talks With Huawei on Autonomous Driving Unit