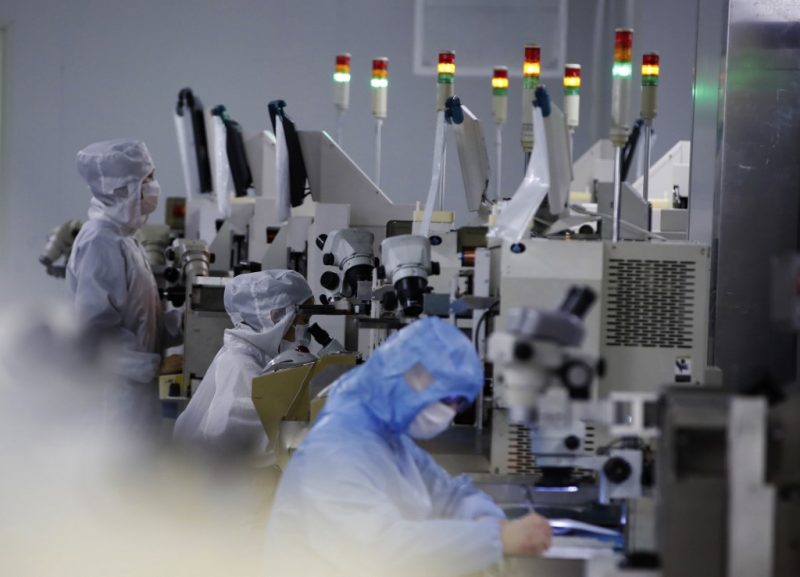
China’s factory inflation in February eased to the slowest annual pace in eight months due to seasonal effects from the Lunar New Year holiday, but analysts expect it to rise in the coming months because of surging global commodity prices.
The producer price index (PPI) increased 8.8% on year, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said in a statement on Wednesday, easing from 9.1% growth in January and slightly higher than a 8.7% rise in a Reuters poll.
Many Chinese factories closed in the first half of February due to Lunar New Year festivities, putting a temporary leash on demand for raw materials. But the war in Ukraine has since raised concerns of supply disruptions, pushing energy and global commodities prices to decade-highs.
“The surge in global commodity prices following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine will have a much more pronounced impact on the March figures,” Julian Evans-Pritchard, senior China economist at Capital Economics, said.
On Monday, an official at the state economic planner also said China’s efforts to stabilise commodity prices face new challenges due to high prices for coal, natural gas and iron ore because of Covid-19, a monetary policy shift in big economies and geopolitical conflicts.
The main drivers for PPI last month were higher prices of oil, gas and iron ore, official data showed.
China sources more than 70% of its oil and 40% of its gas from overseas even as the government races to increase domestic output.
Commodity Price Surge Limits Space for Easing
Some analysts said the scope for monetary easing may be limited due to the threat of higher commodity prices.
“Sanctions on Russia could axe China-Russian trade activities and may lead to higher imported prices,” said Bruce Pang, head of macro and strategy research at China Renaissance Securities.
“Surging commodities prices could fuel China’s PPI inflation and limit China’s space of monetary easing.”
China’s consumer price index (CPI) inched up 0.9% in February, the data showed, unchanged from the growth in January and market expectations.
The Chinese government left its 2022 CPI target, unveiled on Saturday, at around 3%, unchanged from 2021. Last year, the CPI rose just 0.9%, reined in by cautious consumer spending weakened by a slowing economy and domestic Covid-19 outbreaks.
China is targeting slower economic growth of around 5.5% in 2022, with the government citing multiple headwinds at home and abroad.
- Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO READ:
China Factory Growth Rises, But Ukraine Crisis Poses Risks
China Factory Output Up in November As Bottlenecks Ease
China Factory Prices Surge 13.5%, Highest in 26 Years