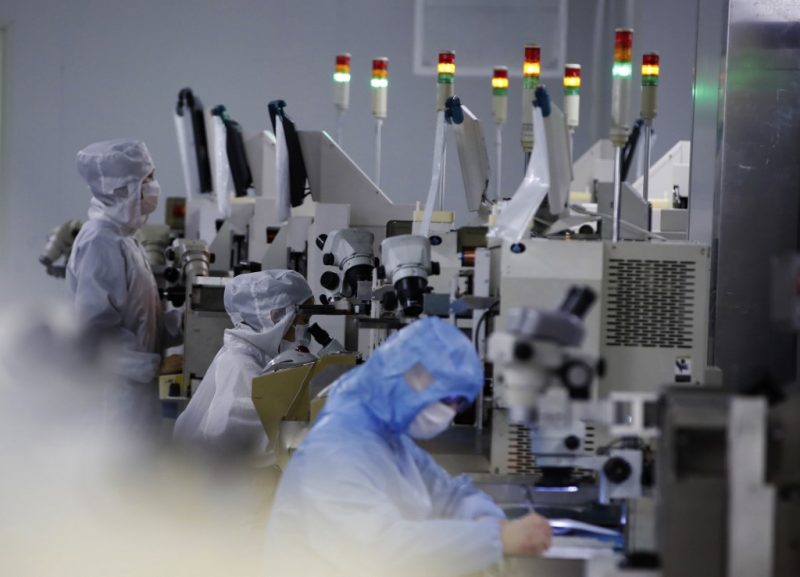
Universities and research institutes in China have been able to buy high-end Nvidia artificial intelligence chips via resellers, despite stronger US curbs imposed by Washington late last year.
A review of hundreds of tender documents by Reuters shows 10 Chinese entities acquired advanced Nvidia chips embedded in server products made by Super Micro Computer, Dell Technologies and Taiwan’s Gigabyte Technology after the US on November 17 expanded the embargo to subject more chips and countries to licensing rules.
Specifically, the servers contained some of Nvidia’s most advanced chips, according to the previously unreported tenders fulfilled between November 20 and February. 28. While the US bars Nvidia and its partners from selling advanced chips to China, including via third parties, the sale and purchase of the chips are not illegal in China.
ALSO SEE: Huawei’s China-Made 7nm Chip ‘Years Behind US’, Raimondo Says
The 11 sellers of the chips were little-known Chinese retailers. Reuters could not determine whether, in fulfilling the orders, they used stockpiles acquired before the US tightened chip-export restrictions in November.
Nvidia said the tenders specify products that were exported and widely available before the restrictions. “They do not indicate that any of our partners violated the export control rules and are a negligible fraction of the products sold worldwide,” a spokesperson said.
The server makers said they complied with applicable laws or would investigate further.
Among the buyers were the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Shandong Artificial Intelligence Institute, Hubei Earthquake Administration, the Shandong and Southwest universities, a tech investment firm owned by the Heilongjiang provincial government, a state-run aviation research centre, and a space science centre.
None of the Chinese buyers and retail sellers responded to questions about the matter.
Daniel Gerkin, a Washington-based partner at law firm Kirkland & Ellis, said Nvidia chips could have been diverted to China without a manufacturer’s knowledge, given a lack of visibility into downstream supply chains.
If the manufacturer had performed sufficient due diligence, “it presumably would be challenging for the US government to pursue an enforcement action”, he said.
The US Commerce Department said it could not comment on any potential ongoing investigations, but said its Bureau of Industry and Security monitored diversions of restricted chips, conducted end-use checks and examined potential breaches.
Officials would investigate credible allegations of violations, including through the use of shell companies, a spokesperson said.
Nvidia said systems built with its graphic processing units (GPUs) – chips that break computer tasks into smaller pieces and process them together – and resold by third parties must comply with US restrictions.
“If we determine that any product was subsequently resold in violation of US export control rules, we’ll work with our customers to take appropriate action,” the spokesperson said.
Super Micro, Dell, Gigabyte deny wrongdoing
Super Micro said it complied with US requirements on the sale and export of GPU systems to regions and parties that require licences.
“If we become aware that a third party has exported or reexported without the required licences, we investigate the matter and take appropriate action,” it said.
In a letter on behalf of Super Micro, US law firm Clare Locke said its client “goes above and beyond what US export restrictions require” by proactively taking steps to ensure its customers do not violate the curbs.
In relation to the tenders that identified its products, Super Micro said they represent “older generation or general purpose servers not capable of the largest-scale AI operations that were available in China prior to the export control regulations”. The awarded suppliers “are not known Supermicro customers”, the company said.
A Dell spokesperson said the company “found no evidence of shipping products configured with the restricted chips you listed to the entities you named”, but that it would continue to investigate.
“Our distributors and resellers are required to comply with all applicable global regulations and export controls. If we become aware of a distributor or reseller that is not complying with these obligations, we take appropriate actions, including termination of our relationship,” the spokesperson said.
Gigabyte said in an email that it complied with Taiwanese laws and international regulations. It did not respond to subsequent questions about tenders that identified its products as a source of banned Nvidia chips. Taiwan’s economy ministry said it expected Taiwanese companies to respect US export controls.
Sales found on public databases
The transactions were disclosed in a dozen of the tenders, which Reuters found on public databases that cover only a fraction of purchases by China’s state entities.
But the small snapshot shows China still has access to advanced chips that US officials say could support AI for military applications, such as the modernisation of China’s defence forces or for developing weapons like hypersonic missiles.
Each of the purchases were limited to several servers and several dozen banned chips. Still, they could be useful for training models and conducting advanced research, according to seven analysts and industry executives.
The tenders – valued at between 71,500 yuan and 1.86 million yuan, or about $10,000 and $259,000 – did not specify the intended uses.
Under Chinese law, procuring agencies representing state or state-affiliated buyers must check that a supplier can fulfill the tender before it is announced as the winner and a contract is signed.
Reuters only analysed tenders whose winners had been announced.
Companies and people accused of violating US export controls can face civil or criminal penalties in the US, including fines of hundreds of thousands of dollars and up to 20 years in prison for individuals.
Reuters last year reported that an underground trade in Nvidia chips had emerged in China, as evident at Shenzhen’s Huaqiangbei electronics market in June, before the US widened its curbs.
On a return visit in December, the vendors who had spoken to Reuters months earlier had gone, and other sellers said they did not know why they left.
Reuters couldn’t establish why the vendors were no longer at the market.
- Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO SEE:
US Releases Detailed Rules For Export Curbs on AI Chips to China
US ‘Drawing Up List of Sanctioned Advanced Chinese Chip Fabs’
China Bans Government Computers From Using Intel, AMD Chips: FT
China’s Retaliatory Bans Could Cost US Tech Giants Billions
China’s SMIC May Have Breached US Curbs With Huawei Chip
Beijing’s Push to Dump Foreign Tech on Display at China Chip Fair
Global Chip Sector ‘Can Never Return to its Pre-Covid Set-up’
US Curbs Set Off Sales, Tech Boom for China Chip Equipment Firms
Banned Nvidia Chips Available in China’s Underground Markets