China’s factory activity rose in September but service sector growth slowed as the economy battled low demand and Covid restrictions.
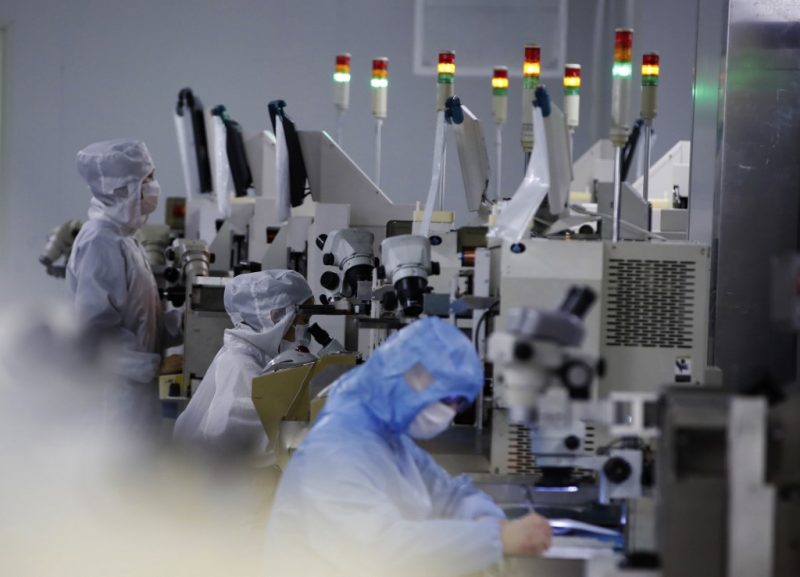
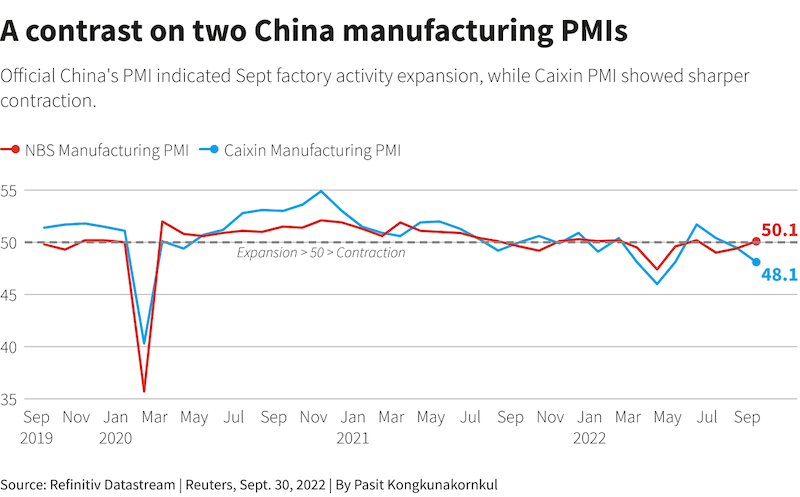
The country’s official manufacturing purchasing managers’ index (PMI) was 50.1 in September, up from contractions in August and July, according to the National Bureau of Statistics.
That figure was ahead of expectations and helped by recent easing measures. Indeed, China’s government has rolled out more than 50 policy measures since late May.
However, a private Caixin survey showed factory activity slumped more quickly in September and and the official survey showed a sharp slowdown in service sector activity growth.
Signs that the world’s second-largest economy is struggling to warm up after narrowly avoiding contraction in the second quarter, could add to concerns about a global recession, as major central banks embark on the most aggressive round of rate rises in decades.
“The surveys suggest that China’s economy continued to lose momentum in September, with the global downturn weighing on exports and virus disruptions dealing a fresh blow to services activity,” Zichun Huang, an economist at Capital Economics, said in a note.
Elsewhere in Asia, data showed South Korea’s factory production shrinking for a second month in August, but a separate release showed Japan’s factories ramping up output again last month.
Also on AF: China’s PBOC Backs Mortgage Rate Cuts to Lift Property Sector
Heatwaves, Covid, Weaker Yuan
“With the basket of economic policies coming into effect and the impacts of heatwaves fading, the manufacturing sector has picked up, leading to the PMI return to expansionary territory,” Zhao Qinghe, a senior statistician at the National Bureau of Statistics, said in a statement.
Covid outbreaks dragged down businesses in retail, aviation, accommodation and catering sharply, Zhao said, adding that a government-led infrastructure push accelerated construction activity.
The official survey showed non-manufacturing PMI falling to 50.6 in September from 52.6 in August. The official composite PMI, which includes manufacturing and services, fell to 50.9 from 51.7.
The private Caixin survey also released on Friday showed factory activity contracted at a sharper pace in September, with indexes for output, new orders and employment all declining due to weak demand. The Caixin survey typically covers smaller, export-oriented companies.
The releases come as the yuan hit its weakest level since the global financial crisis in 2008 this week even as the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) made betting against the yuan more expensive and warned against speculative yuan trading.
“Pressure on the yuan also means that the PBOC is constrained in its ability to provide monetary support,” Huang added.
Weak Demand
The official manufacturing PMI survey showed the new export orders index dropping to 47.0 from 48.1 in August, a trend also reflected in the private Caixin survey. External demand has been hit by rising interest rates, high inflation and the war in Ukraine.
“(The) export order index eased further … pointing to weakening external demand as the monetary policy tightening has brought in recession concerns in the developed economies,” said Zhou Hao, chief economist at Guotai Junan International.
“If the external demand weakens further, the Chinese economy will have to turn more emphasis to domestic demand.”
The official manufacturing survey also showed new orders and employment shrinking, albeit more slowly, amid stricter coronavirus curbs in multiple cities including Shenzhen and Chengdu.
The release is one of the last official economic indicators to be announced before China’s ruling Communist Party Congress in mid-October.
- Reuters, with additional editing from Alfie Habershon and Jim Pollard
Read more:
China Plans $347bn in Treasury Bonds, Plus Infra Loans
Banks Eye China Divestments, India and SE Asia for M+A Deals