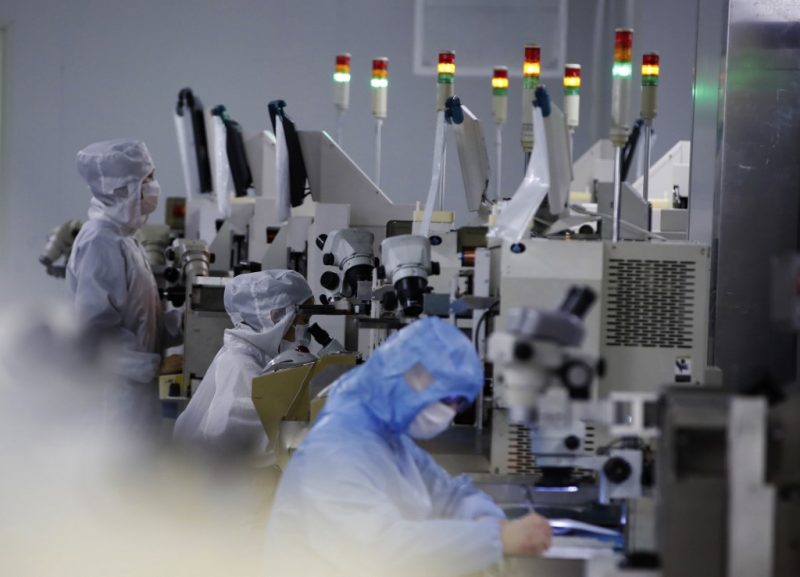
Factory activity in China suffered an unexpected fall in May, as the country’s long-running property crisis continues to undermine business and consumer outlook.
Data from the National Bureau of Statistics on Friday showed that the official manufacturing purchasing managers’ index (PMI) dropped to 49.5 in May from 50.4 in April.
The disappointing number, below the 50-mark separating growth from contraction, was well under analysts’ forecast of 50.4. It adds to a series of recent indicators showing the $18.6 trillion economy is struggling to get back on its feet, eroding optimism seen after better-than-expected output and trade data.
ALSO SEE: After Chips, China to Pour Millions Into Solid-State Batteries
“I think the data particularly reflects soft domestic demand, the housing sector continued to worsen and retail sales were not strong,” Xu Tianchen, senior economist at the Economist Intelligence Unit, said.
“The May reading may indicate a temporary blip. We’ll probably see an improvement in June as new government policies start to impact, such as the property rescue plan and the issuance of special sovereign bonds,” he added.
Retail sales down, jobs shrinking
The PMI’s sub-indices for new orders and new export orders both tipped back into contraction after two months of growth, while employment continued to shrink.
The services sub-index under the NBS non-manufacturing survey improved to 50.5 in May from 50.3 in April. But growth as represented by the broader services index, which also includes construction, slowed in May to 51.1 from 51.2 a month prior.
Problems in the property sector have had a negative impact across broad areas of China’s economy and slowed Beijing’s efforts to shift its growth model more towards domestic consumption from debt-fuelled investment.
Retail sales grew last month at their slowest since December 2022 while new home prices fell at their fastest rate in nine years, suggesting it is too early to say if the battered economy has finally turned a corner.
The International Monetary Fund on Wednesday revised up its China growth forecast by 0.4 percentage points to 5% for 2024 and 4.5% in 2025, but warned the property sector remained a key growth risk.
China this month unveiled “historic” steps to stabilise the property market, but analysts say the measures fall short of what is required for a sustainable recovery.
The IMF said it saw “scope for a more comprehensive policy package to address property sector issues.”
Nie Wen, an economist at Shanghai Hwabao Trust, said the decline reinforced the case for more support.
“There is still a need to strengthen stimulus on the demand side, while at the same time sorting the credit channels as soon as possible to avoid financial institutions’ balance sheets shrinking, which would have a negative effect on the economy,” Nie said.
- Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO SEE:
Chinese Censors Block ‘Wealth Flaunting’ on Social Media – NBC
Global Funds Proving Popular in China as the Yuan Weakens
After Much Planning, China’s EV Makers Set to Storm Europe
China Pins Hopes on ‘Heavyweight’ Property Sector Rescue Bid
China’s ‘White-List’ Makes Little Headway Amid Property Gloom