China’s crackdown on borrowing by private developers has hit demand at urban land auctions and put a squeeze on regional finances. This is forcing provincial governments to find other income sources to fund investments and support the economy.
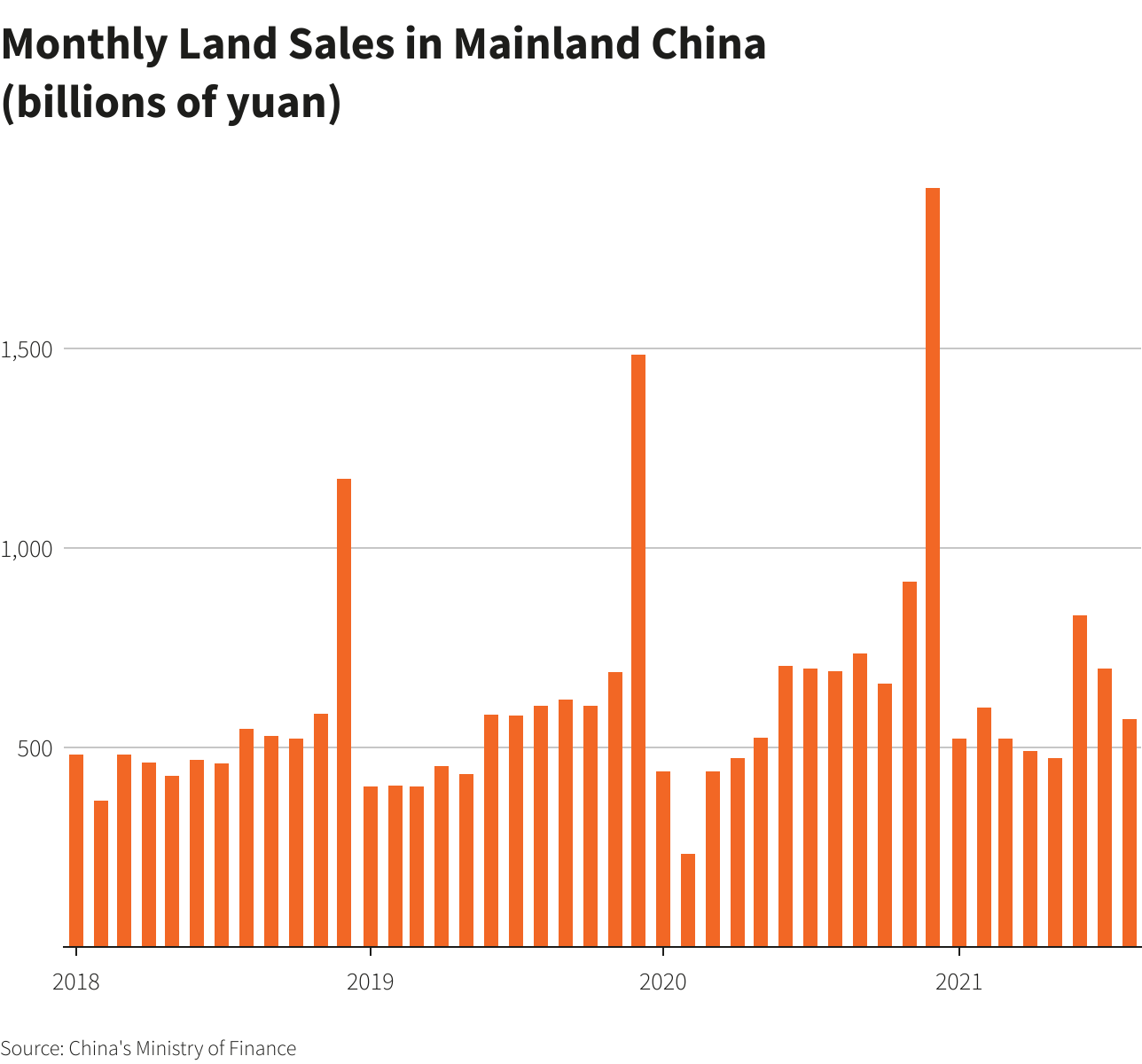
Land sales soared to a record 8.4 trillion yuan ($1.3 trillion) in 2020, the equivalent of Australia’s annual gross domestic product, bolstering local fiscal budgets in a pandemic year.
But tighter regulations on borrowing by private developers since the summer of last year are increasingly eroding demand for land. The value of nationwide land sales abruptly fell 17.5% year-on-year in August, according to Reuters calculations of finance ministry data, the biggest slide since February 2020.
Further falls could force regional governments, who on average depend on land sales for a fifth of their revenue, to cut spending and investment. Many economists have already downgraded China’s 2021 GDP growth forecast, due to a cooling property market and contagion risks from indebted property behemoth China Evergrande.
To boost incomes, some local governments may be driven to issue more bonds, increasing their debt obligations. They may even hasten plans for a controversial property tax, analysts say.
“In general, the proportion of land sales revenue for local governments in China is quite large, at over 20%, so if land sales decline, or their growth slows, local government spending will see a certain amount of pressure,” Betty Wang, senior China economist at ANZ in Hong Kong, said.
Falling Demand
In an attempt to better control land prices in the country’s most valuable locations, and by extension, prices of finished homes, authorities said in February that China’s 22 biggest cities can only conduct three rounds of land auctions this year.
The authorities have also since put a cap on the highest bids to contain prices, as part of a vast crackdown across sectors as President Xi Jinping seeks to correct excesses and imbalances in China’s economy and society.
But since the first round of auctions in March-June, demand has fallen as cash-strapped developers stayed away.
In an ongoing round of auctions in June-October, about 40% of the plots on offer were withdrawn or had no bidders as of September 30, a Reuters analysis of more than 1,000 public notices showed. That compared with 5% of untaken offers in the first round.
Tianjin in northern China sold 40 out of 61 plots, while Shenyang, the provincial capital of Liaoning, offloaded 19 of 46 lots, the analysis showed.
Moody’s predicts land sales growth will be in the low single-digits in 2021 before declining in 2022. Sales grew 16% last year.
To offset poorer land sales, local governments could issue more bonds, but that would raise the prospect of a higher debt burden, Moody’s warned in a report.
Highly-indebted Tianjin and Liaoning may struggle to meet debt obligations if land sales worsen, according to Moody’s.
State Support
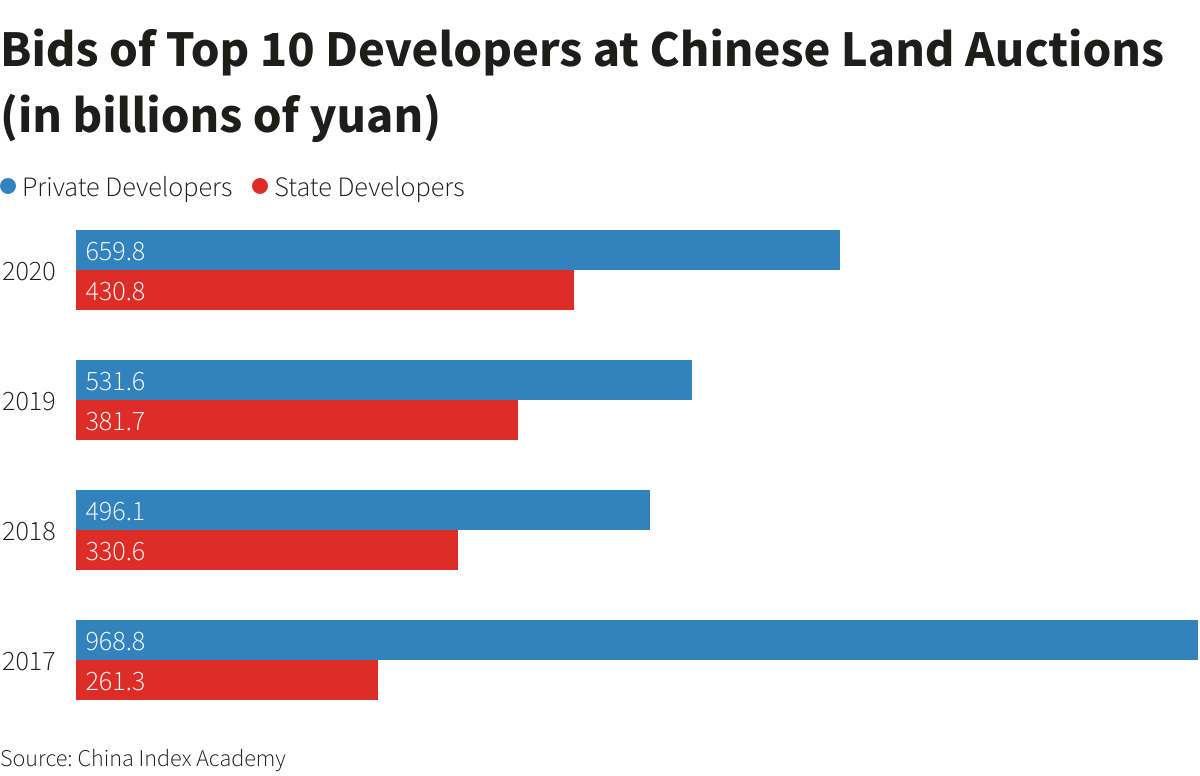
State firms have dominated land auctions as private developers stuck to the sidelines, but it is uncertain whether this would be enough to safeguard local government revenues.
The value of winning bids by state firms have been triple that of private developers in the June-October auctions so far, marking a departure from past trends. But, as of September 30, the value of their overall bids was down 45% to 277.2 billion yuan from the March-June auctions.
In the southwestern megacity of Chengdu, state-controlled China Railway Construction Corp placed bids for 15 plots of land and put down a whopping deposit of 4.28 billion yuan ($662 million).
In contrast, private developers such as Fantasia Holdings Group and China Fortune Land Development have spent less on land purchases this year than in 2020, or nothing at all, according to the analysis. Evergrande, through a local developer, bought only one plot this year in June, the analysis showed.
The companies did not respond to requests for comment.
Seven out of China’s 22 biggest cities have until the end of October to auction land, including Beijing, Shanghai and Hangzhou.
Longer term, local governments may seek other sources of fiscal revenue such as property taxes to offset fluctuating real estate markets, ANZ’s Wang said.
China has mulled a nationwide property tax for over a decade but faced resistance from stakeholders including local governments themselves, who fear it would erode property values or trigger a market sell-off.
“Start with the pilots, and rules can be adjusted accordingly,” she said.
• Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO SEE:
China Developers Facing Worst Debt Crisis In A Decade
Evergrande debt crisis explained
























