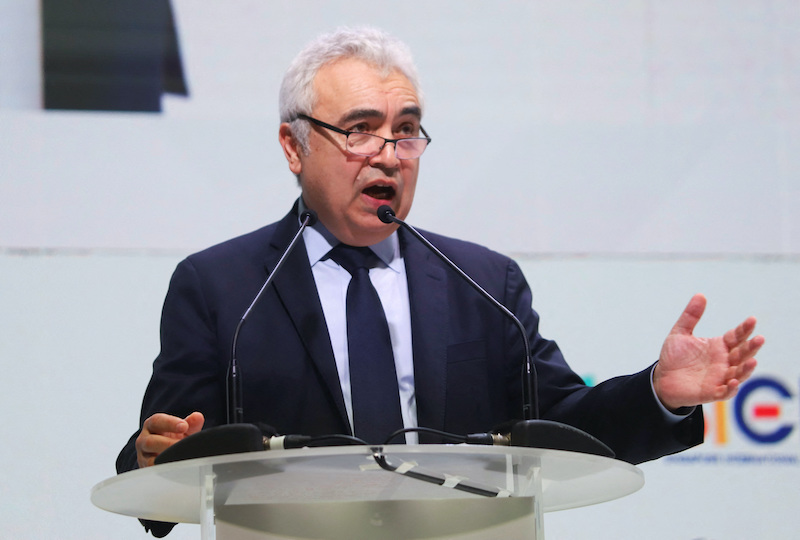
The world is facing its “first truly global energy crisis” and still needs Russian oil, according to Fatih Birol. But the head of the International Energy Agency said the positive side to the crisis is that is spurring a faster transition to clean, renewable sources of power.
Birol said the energy crisis could be a turning point for accelerating clean sources and for forming a sustainable and secured energy system.
“Energy security is the number one driver (of the energy transition),” said Birol, as countries see energy technologies and renewables as a solution.
Indeed the IEA has upgraded its forecast of renewable power capacity growth in 2022 to a 20% year-on-year increase from 8% previously, with close to 400 gigawatts of renewable capacity being added this year.
Many countries in Europe and elsewhere were accelerating the installation of renewable capacity by cutting the permitting and licensing processes to replace the Russian gas, Birol said.
ALSO SEE: China’s Yuan Drops Near 15-Year Low After Investors’ Selloff
OPEC Cuts ‘Risky’ and ‘Unfortunate’
In a speech in Singapore on Tuesday, Birol expressed alarm about tightening markets for liquefied natural gas and sharp supply cuts announced by major oil producers.
He warned that rising imports of LNG to Europe amid the Ukraine crisis and a potential rebound in Chinese appetite for the fuel would tighten the world market because only 20 billion cubic metres of new LNG capacity be added next year.
Birol said the recent decision by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies, known as OPEC+, to cut 2 million barrels per day (bpd) of output was “risky” and “really unfortunate”, because the IEA sees global oil demand growing to close to 2 million barrels per day this year.
“(It is) especially risky as several economies around the world are on the brink of a recession, if that we are talking about the global recession…I found this decision really unfortunate.”
Soaring global prices across a number of energy sources, including oil, natural gas and coal, are hammering consumers at the same time they are already dealing with rising food and services inflation.
‘Russian Oil Still Needed’ Amid Concern on European Winter
The high prices and possibility of rationing are potentially hazardous to European consumers as they prepare to enter the Northern Hemisphere winter. Europe may make it through this winter, though somewhat battered, if the weather remains mild, Birol said.
“Unless we will have an extremely cold and long winter, unless there will be any surprises in terms of what we have seen, for example, Nordstream pipeline explosion, Europe should go through this winter with some economic and social bruises,” he added.
For oil, consumption is expected to grow by 1.7 million bpd in 2023 so the world will still need Russian oil to meet demand, Birol said.
G7 nations have proposed a mechanism that would allow emerging nations to buy Russian oil but at lower prices to cap Moscow’s revenues in the wake of the Ukraine war.
Birol said the scheme still has many details to iron out and will require the buy-in of major oil importing nations.
A US Treasury official said last week that it is not unreasonable to believe that up to 80% to 90% of Russian oil will continue to flow outside the price cap mechanism if Moscow seeks to flout it.
“I think this is good because the world still needs Russian oil to flow into the market for now. An 80%-90% is good and encouraging level in order to meet the demand,” Birol said.
While there is still a huge volume of strategic oil reserves that can be tapped during a supply disruption, another release is not currently on the agenda, he added.
- Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO SEE:
Australia and Japan Ramp up Security Ties, Energy Focus
China, Saudi Arabia Pledge Closer Energy Cooperation